Wastewater treatment
in the wood-based panel industry
Wastewater treatment
Since competition for water as a resource is expected to rise significantly in the coming decades and efforts to use freshwater sparingly are, therefore, becoming increasingly important, wastewater treatment in the wood-based panel industry is growing in importance. Wastewater treatment plants from SCHRADER are the optimal solution for the increasingly strict public government regulations (e.g. Water Framework Directive), from both an ecological and an economic point of view: they work without residues, since the residual materials from one process stage are the feed for another process stage, even if the individual processes are separated in time or space.
Mechanical pre-treatment
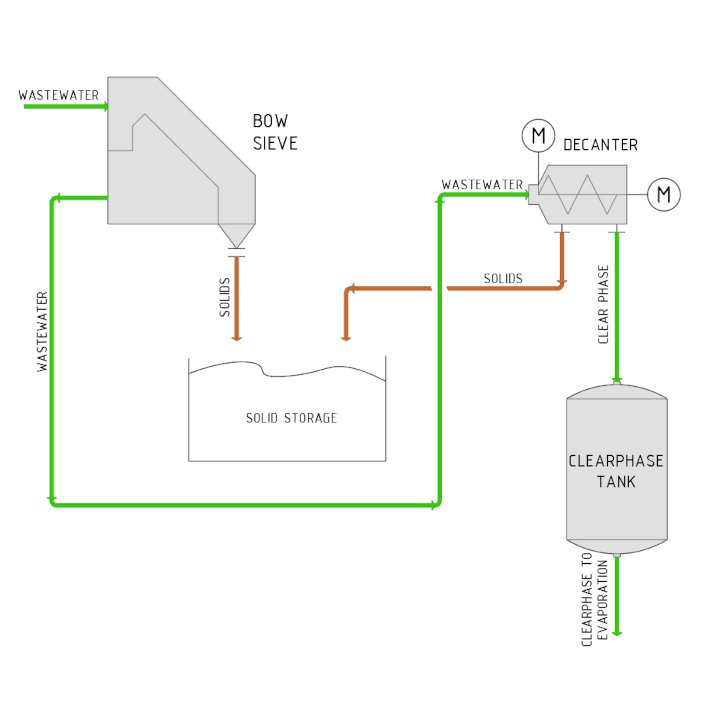
In mechanical pre-treatment, the wastewater is separated from the solids in order to protect the evaporation plant from blockages, deposits and wear.
The mechanical pre-treatment consists of two treatment stages connected in series: the bow sieve for coarse solids and the decanter centrifuge for fine solids. The water out of the wood, along with other production wastewater, is passed over the bow sieve in order to separate out any particles > 3mm. These are then fed into the solids storage. As an option, the solids can be pressed in a FAN separator. The sieved wastewater is collected in a buffer tank, from where it is pumped into the decanter to separate the finer solids > 1mm by centrifugal force. Any solids separated at this stage are also fed into the solids storage. All filter residues collected here are fed to the energy plant for thermal recycling and incinerated without leaving behind any residues. The pre-treated wastewater is collected in the clear phase vessel and prepared for evaporation.
SCHRADER Supervision
By using the latest data technology, it is possible to optimally support the operation of the technical plants with minimal effort. The data transparency thus created increases the diagnostic possibilities and has a positive effect on the operating efficiency of the system and the maintenance activities.
Mechanical pre-treatment: separation of wood components > 1mm in the water
- Removal of particles > 3 mm from the process wastewater by means of a bow sieve
- Fine separation of turbid materials > 1 mm by means of a decanter centrifuge
- Supply of treated wastewater for evaporation
- Supply of solid materials for incineration
Evaporation
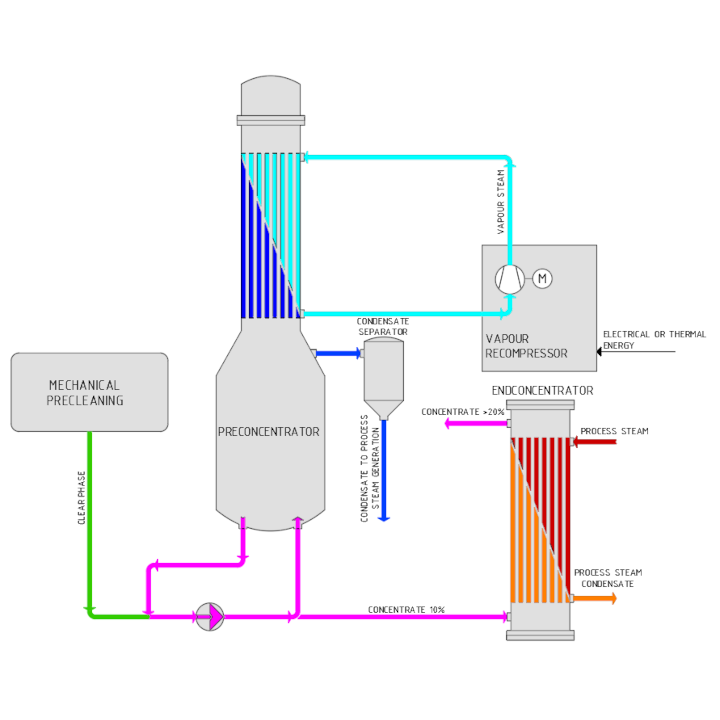
Wastewater contaminated with organic matter passes from the clear phase vessel into the falling film evaporator, which is divided into two compartments. The evaporator then concentrates the remaining organic matter from 1-2 wt% to approx. 10 wt% and feeds this into the end concentrator. During the entire wastewater treatment process, the falling film evaporator is heated by its vapours and the vapour produced in the end concentrator, which are jointly brought to a higher energy level in the vapour re-compressor. In order to make use of this energy-efficient mode of operation, continuous plant operation is necessary, as each start-up must be carried out by supplying process steam.
The desired concentration of organic matter (20 – 30wt%) is achieved in the end concentrator, which consists of a forced circulation evaporator with an integrated round or flat tube heat exchanger. This end concentrate is also fed into the energy plant for thermal recycling.
The resulting condensate from the falling film evaporator is reused in the process steam generation. This ensures the residue-free treatment of production wastewater.
Evaporation: Evaporation of water to produce condensate as feed for process steam generation
- Concentrates wastewater to 10% dry substance without end concentrator or 30% dry substance with end concentrator
- Use of the vapour as a heating medium by means of mechanical vapour recompression (MVR)
- Supply of the concentrate for combustion
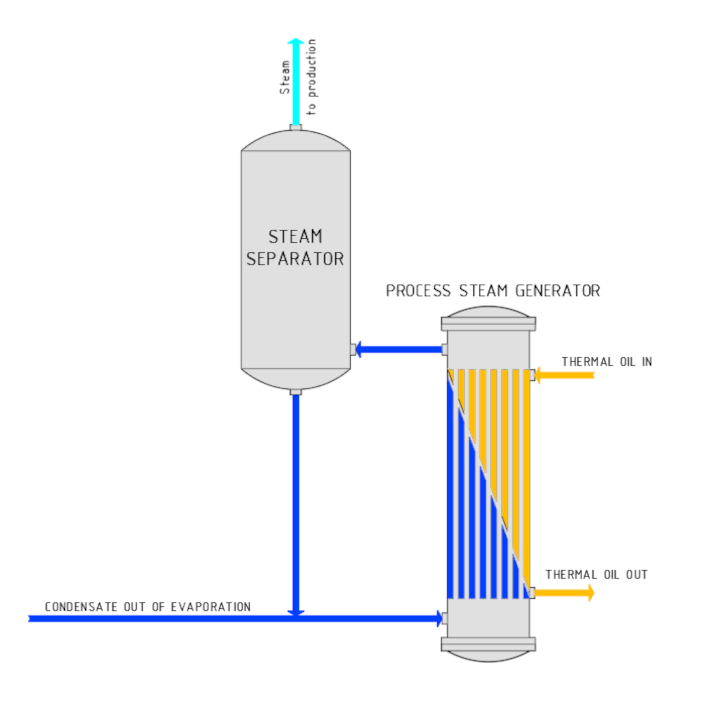
Process steam generation
A steam generator is used to generate process steam; this operates on the natural circulation principle and is heated using thermal oil or live steam. The steam generator consists of a round tube heat exchanger arranged vertically and a steam separator.
The condensate collected from the evaporation plant is used as feed water, with soft water added where required. Almost all of the process steam is fed into the wood-based panel production plant, while a small portion is used to heat the pre-concentrator and final concentrator in the evaporation plant.
Contact
Our global network of experienced engineers is available to you by phone or e-mail. Don’t hesitate to get in touch.